Ever wondered what happens when you upload a video to YouTube? From your device to data centers across the globe, YouTube employs groundbreaking technology to ensure billions of videos are accessible anytime, anywhere. Let’s take a deep dive into the journey of a YouTube video!
Uploading a Video: The Journey Begins
When you hit the upload button, YouTube starts processing your video immediately.
- Data Ingestion Pipelines: The upload process begins with a data ingestion pipeline that handles incoming video files. YouTube uses Google Cloud APIs to facilitate this process, allowing users to upload videos in chunks. This method not only makes uploads faster but also more reliable.
- Data Validation: Before the video is sent to storage, YouTube checks if the file is valid and safe. This involves scanning for any prohibited content and ensuring the file format is supported.
Video Transcoding: Making Videos Accessible Everywhere
Transcoding is crucial for ensuring that videos can be viewed on various devices and connection speeds.
- What is Transcoding?: It involves converting videos into multiple resolutions and formats. For instance, your 4K video is transcoded into resolutions like 1080p, 720p, and 480p. This allows YouTube to serve the best quality based on the viewer’s device and internet speed.
- Video Codecs: YouTube utilizes advanced codecs like VP9 and H.264 for compression. These codecs enable high-quality streaming while minimizing bandwidth usage.
Video Storage: Handling Billions of Files
YouTube’s storage solution is designed to manage vast amounts of data efficiently.
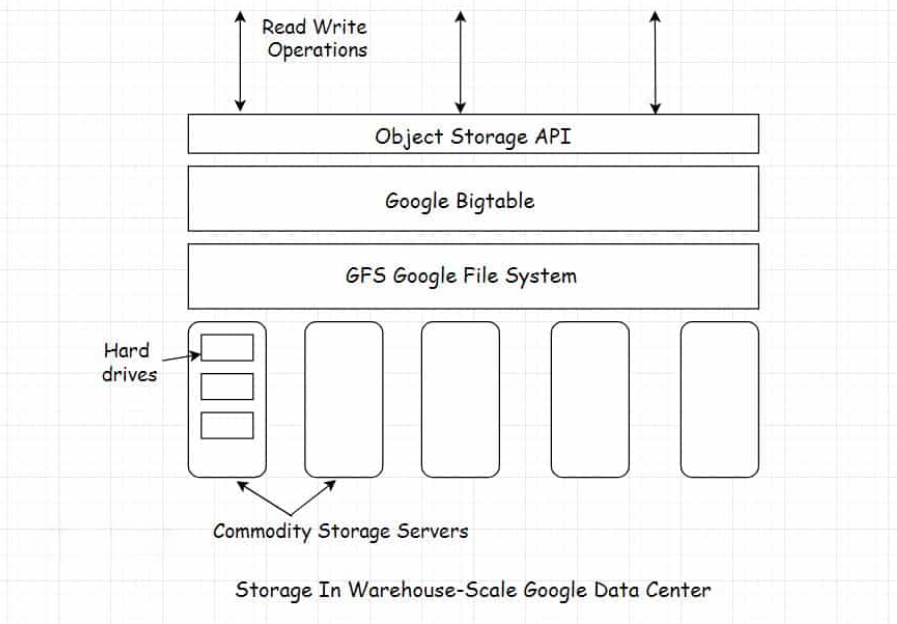
- Distributed Storage Systems: Videos are stored across multiple servers worldwide using Google’s Colossus File System. Think of it as storing puzzle pieces across different locations and putting them back together when needed.
- Redundancy and Reliability: To prevent data loss, YouTube employs replication strategies. Fun fact: your video has multiple backups in data centers around the globe!
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: Smooth Playback for All
Adaptive Bitrate (ABR) streaming is key to providing a seamless viewing experience.
- What is ABR Streaming?: This technology adjusts video quality based on the viewer’s internet speed. If your connection slows down, you might notice the video automatically switches to a lower resolution—this is ABR in action.
// Example of ABR manifest logic
const manifest = {
"video": [
{"resolution": "1080p", "bitrate": "3000kbps"},
{"resolution": "720p", "bitrate": "1500kbps"},
{"resolution": "480p", "bitrate": "800kbps"}
]
};
Algorithms Behind the Scenes
YouTube employs sophisticated algorithms for both compression and recommendations.
- Compression Algorithms: To maintain quality while reducing file sizes, YouTube uses codecs like VP9, AV1, and H.265. These algorithms ensure efficient storage and transmission of videos without significant quality loss.
- Recommendation Algorithms: Machine learning models analyze user behavior to suggest videos using techniques like collaborative filtering and deep neural networks.
The Programming Languages That Power YouTube
YouTube’s backend is built using several programming languages tailored for specific tasks:
- Backend Languages: C++ and Java are used for performance-focused tasks, while Python plays a significant role in various functionalities due to its simplicity and flexibility.
- Frontend Technologies: JavaScript and TypeScript are employed for creating user interfaces, often using frameworks like AngularJS.
- AI and Machine Learning Tools: TensorFlow and Python are utilized for developing machine learning models that enhance user experience through personalized recommendations.
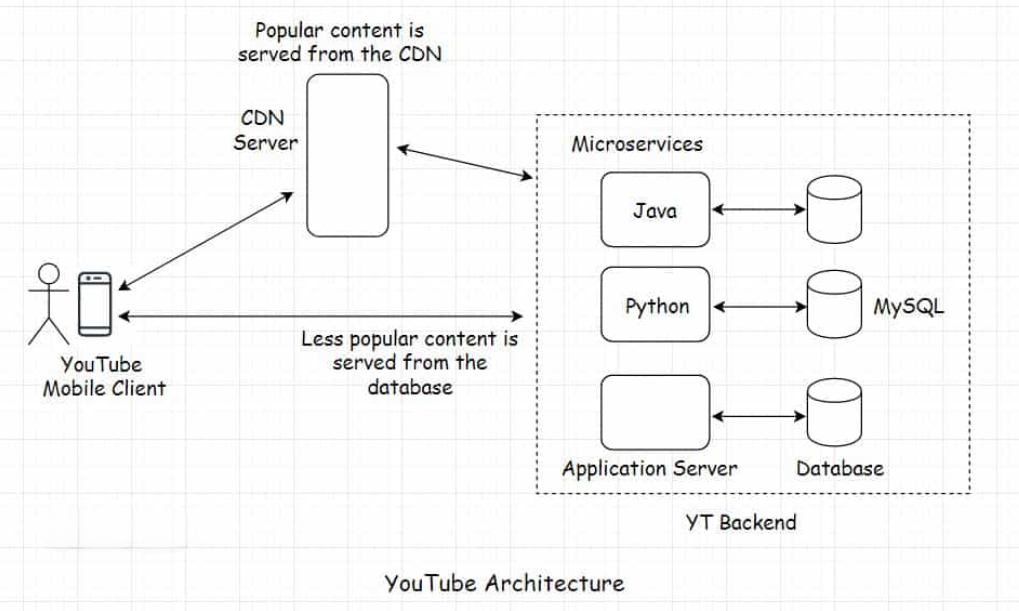
The Role of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs are vital for ensuring fast video delivery worldwide.
- What are CDNs?: Content Delivery Networks cache video content on edge servers located closer to users, significantly reducing latency and improving load times. When you request a video, it’s served from the nearest CDN node rather than from distant data centers.
Security and Scalability: Protecting Your Videos
Security measures are critical in protecting user content.
- Encryption: Videos are stored securely using encryption techniques that safeguard against unauthorized access.
- Scalability: YouTube’s infrastructure dynamically scales to handle spikes in traffic, such as during viral events. This ensures that even during peak times, users can access their favorite content without interruption.
Conclusion
Behind every play button is a fascinating blend of technology and innovation. From transcoding to delivery, YouTube’s video system is a marvel of modern computing. The next time you upload or stream a video, remember the magic happening in the background!












