Google Drive has become an essential tool for individuals and businesses alike, providing a seamless way to store, share, and collaborate on files. But how does it work behind the scenes? This blog post will explore the inner workings of Google Drive, focusing on its data management, security features, and the technologies that power it.
How Does Google Drive Work Behind the Scenes?
Understanding how Google Drive operates can demystify the process of file storage and retrieval.
Uploading and Storing Data
When you upload a file to Google Drive:
- File Segmentation: The file is divided into smaller chunks.
- Encryption: Each chunk is encrypted using unique keys before being sent to Google’s servers.
- Distribution: The encrypted chunks are stored across multiple data centers worldwide. This not only enhances security but also ensures redundancy—if one server fails, your data remains accessible from another location.
- Indexing: Google indexes the files so they can be quickly retrieved when needed.
Retrieving Data
When you access a file:
- Request Handling: Your request is routed through Google’s load balancers, which distribute incoming traffic efficiently across servers.
- Decryption: The relevant encrypted chunks are retrieved and decrypted using the stored keys.
- Reassembly: The chunks are reassembled into the original file format before being sent back to you.
This process allows users to access their files almost instantaneously, regardless of where they are stored.
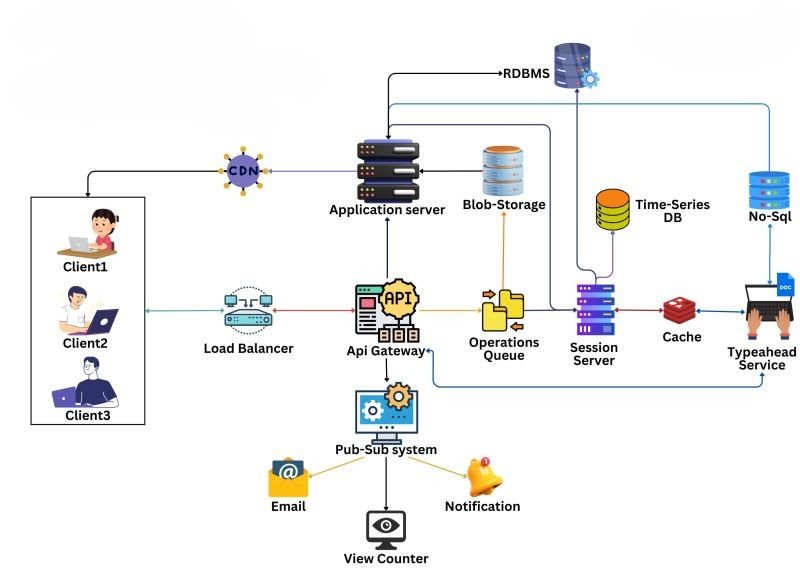
Languages & Techniques Powering Google Drive
Google Drive’s backend is powered by a variety of programming languages and technologies designed for efficiency and scalability.
Programming Languages
- Python: Widely used for its readability and ease of use, Python plays a significant role in developing backend services for Google Drive.
- C++: Known for its performance efficiency, C++ is also utilized in components that require high-speed processing and resource management.
- Java: Java’s portability makes it suitable for various applications within Google’s ecosystem, ensuring that services can run seamlessly across different platforms.
Database Management
Google employs its proprietary database system called Spanner.
- Redundancy: Spanner ensures that data is replicated across multiple locations, providing high availability and fault tolerance.
- Real-Time Consistency: It uses advanced algorithms to maintain consistency across distributed systems, allowing users to access up-to-date information regardless of where they are located.
Server-Side Technologies
The infrastructure supporting Google Drive involves several advanced server-side technologies designed for reliability and performance.
Load balancers distribute user requests across multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This ensures that users experience minimal delays when accessing their files.
Google Drive utilizes a microservices architecture, which breaks down applications into smaller services that can be developed and deployed independently. This approach allows for:
- Scalability: Services can be scaled according to demand without affecting the entire system.
- Fault Isolation: If one service fails, it does not bring down the entire application, enhancing overall reliability.
Non-Technical Aspects
To make these concepts more relatable, think of Google Drive like a well-organized library:
- Uploading Files: When you add a book (file), it gets categorized (indexed) and placed on shelves (servers) throughout the library (data centers).
- Retrieving Files: When you want to read a book, you ask the librarian (load balancer) who quickly fetches it from wherever it’s stored in the library.
This analogy helps illustrate how efficient systems work behind the scenes to make our digital lives easier.
Is Google Drive Safe for Personal Data?
When considering whether to use Google Drive for personal data storage, security is a top concern.
Data Encryption
Google Drive employs robust encryption methods to protect user data. Files are encrypted both during transmission and while at rest:
- In-Transit Encryption: When you upload or download files, Google uses 256-bit SSL/TLS encryption to secure your data as it travels over the internet.
- At-Rest Encryption: Once your files reach Google’s servers, they are encrypted with 128-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). This means that even if someone were to gain unauthorized access to Google’s servers, they would not be able to read your files without the decryption keys.
Two-Factor Authentication
To further enhance security, Google Drive supports two-factor authentication (2FA). This requires users to provide two forms of identification before accessing their accounts, making it significantly harder for hackers to gain access even if they have your password.
Overall, while no system is entirely foolproof, Google Drive implements multiple layers of security that make it a safe option for personal data storage.
Conclusion
Google Drive’s combination of advanced technology and robust security measures makes it an excellent choice for storing personal data. With features like encryption, two-factor authentication, and a sophisticated backend powered by languages like Python and C++, users can trust that their information is safe and accessible whenever needed.
As we continue to rely on cloud storage solutions like Google Drive in our daily lives, understanding how these systems work can empower us to use them more effectively while ensuring our data remains protected.












